2. Construction of expression matrix
2.1 Visualization: Genome Broswer
2.1.1 Build bedGraph/bigwig files
use BEDtools and UCSC Kent Utilities
# convert sam to bam
samtools view -S -b NC_1.miRNA_hg38_mapped.sam | samtools sort - > NC_1.miRNA_hg38_mapped.bam
# build bam index
samtools index NC_1.miRNA_hg38_mapped.bam > NC_1.miRNA_hg38_mapped.bai
# create bedGraph
bedtools genomecov -ibam NC_1.miRNA_hg38_mapped.bam -bga -split | sort -k1,1 -k2,2n > NC_1.miRNA_hg38_mapped.bedGraph
Note
http://bedtools.readthedocs.io/en/latest/content/tools/genomecov.html
use homer
1.Make tag directories for each experiment
#works with sam or bam (samtools must be installed for bam) makeTagDirectory NC_1.miRNA.tagDir/ NC_1.miRNA_hg38_mapped.sam -format samIf the experiment is strand specific paired end sequencing, add "-sspe" to the end. If it's unstranded paired-end sequencing, no extra options are needed.
makeTagDirectory tags_Dir/ inputfile.sam -format sam -sspe2.Make bedGraph visualization files for each tag directory
# Add "-strand separate" for strand-specific sequencing makeUCSCfile NC_1.miRNA.tagDir/ -fragLength given -o auto (repeat for other tag directories)
2.1.2 Integrative Genomics Viewer(IGV)
in our case, try to load the bam and bigwig format file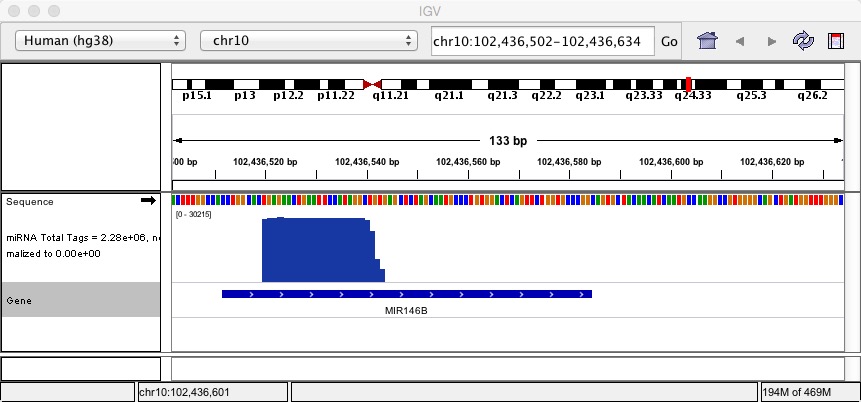
2.1.3 UCSC genome browser

2.2 Quantify gene expression
2.2.1 Concept
raw counts
RPKM: Reads Per Kilobase of exon model per Million mapped reads (每千个碱基的转录每百万映射读取的reads)
FPKM: Fragments Per Kilobase of exon model per Million mapped fragments(每千个碱基的转录每百万映射读取的fragments, 对于Pair-end sequencing, two paired reads should be mapped simultaneously)
RPKM = total exon reads/ (mapped reads (Millions) * exon length(KB))TPM:Transcripts Per Kilobase of exon model per Million mapped reads (每千个碱基的转录每百万映射读取的Transcripts)
TPMi=(Ni/Li)*1000000/sum(Ni/Li+……..+ Nm/Lm)RPM/CPM: Reads/Counts of exon model per Million mapped reads (每百万映射读取的reads)
RPM=total exon reads / mapped reads (Millions)
2.2.2 Required files
- alignment: bam/sam format
convert sam to bam
samtools view -S -b NC1.miRNA_hg38_mapped.sam > NC1.miRNA_hg38_mapped.bam
- annotaion: gtf/gff/gff3 format
convert gff to gtf
gffread tRNA.gff -T -o tRNA.gtf
2.2.3 Tools
the gtf annotation should be match to the genome (index).
in our case, we build index for each RNA types, but the annotaion file (gff/gtf) is matched the position in human genome.
samtools view -bhF 4 NC1.miRNA.sam | bedtools bamtofastq -i - -fq NC1.miRNA_fastq
bowtie2 -p 4 --sensitive-local -x /BioII/lulab_b/shared/genomes/human_hg38/index/bowtie2_hg38_index/GRCh38_p10 NC1.miRNA_fastq -S NC1.miRNA_hg38_mapped.sam
samtools view -S -b NC1.miRNA_hg38_sam > NC1.miRNA_hg38_mapped.bam
* HTSeq
Given a file with aligned sequencing reads(.sam/.bam) and a list of genomic features(.gtf), a common task is to count how many reads map to each feature(gene).
Usage
htseq-count [options] <alignment_files> <gff_file>
in our case
htseq-count -m intersection-strict --idattr=Name --type=miRNA_primary_transcript NC_1.miRNA_hg38_mapped.sam /BioII/lulab_b/shared/genomes/human_hg38/gtf/miRNA.gff > NC_1.miRNA.htseq.counts
- 3 overlap resolution models
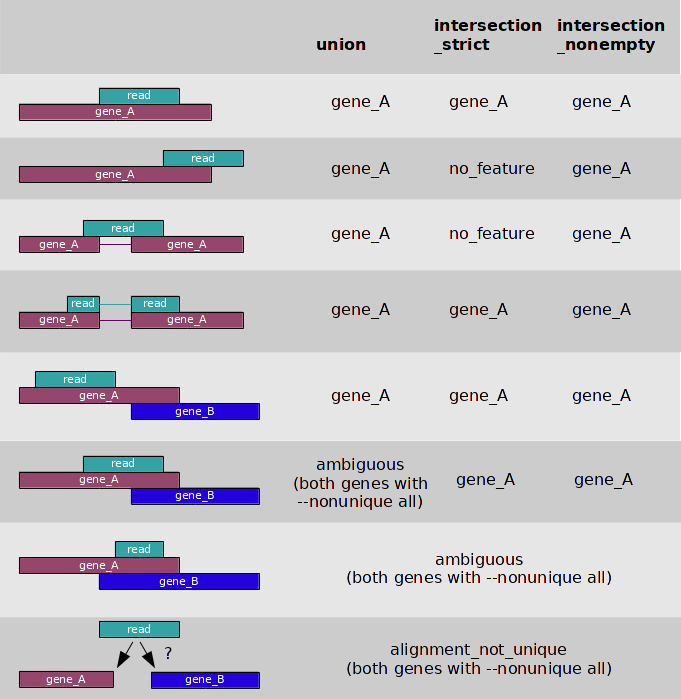
- We shared our snakemake package used for exRNA-seq expression matrix construction.Github.
Tips
- --nonunique
- --nonunique none (default): the read (or read pair) is counted as ambiguous and not counted for any features. Also, if the read (or read pair) aligns to more than one location in the reference, it is scored as alignment_not_unique.
- --nonunique all: the read (or read pair) is counted as ambiguous and is also counted in all features to which it was assigned. Also, if the read (or read pair) aligns to more than one location in the reference, it is scored as alignment_not_unique and also separately for each location.
- Notice that when using --nonunique all the sum of all counts will not be equal to the number of reads (or read pairs), because those with multiple alignments or overlaps get scored multiple times.
Notes
- -m/--mode {mode}
- --nonunique={none/all}
- -s/--stranded {yes/no/reverse}.
- -a {minaqual}.
- -t/--type {feature type}. (defult: exon)
- -i/--idattr {id attribute}, GFF attribute to be used as feature ID. (defult: gene_id)
* featureCounts
Usage
Summarize a BAM format dataset:
featureCounts -t exon -g gene_id -a annotation.gtf -o counts.txt mapping_results_SE.bam
Summarize multiple datasets at the same time:
featureCounts -t exon -g gene_id -a annotation.gtf -o counts.txt library1.bam library2.bam library3.bam
in our case
featureCounts -t miRNA_primary_transcript -g Name -a /BioII/lulab_b/shared/genomes/human_hg38/gtf/miRNA.gff -o NC_1.miRNA.featureCounts.counts NC_1.miRNA_hg38_mapped.bam
Tips
By default, featureCounts does not count reads overlapping with more than one feature. Users can use the -O option to instruct featureCounts to count such reads (they will be assigned to all their overlapping features or meta-features).
* Homer
Usage
0.Align FASTQ reads using STAR or similar 'splicing aware' genome alignment algorithm
1.Make tag directories for each experiment
#works with sam or bam (samtools must be installed for bam) makeTagDirectory Exp1r1/ inputfile1r1.sam -format sam makeTagDirectory Exp1r2/ inputfile1r2.sam -format samIf the experiment is strand specific paired end sequencing, add "-sspe" to the end. If it's unstranded paired-end sequencing, no extra options are needed.
makeTagDirectory Exp1/ inputfile.sam -format sam -sspe2. Quantify gene expression across all experiments for clustering and reporting (-rpkm):
# May also wish to use "-condenseGenes" if you don't want multiple isoforms per gene analyzeRepeats.pl rna hg19 -strand both -count exons -d Exp1r1/ Exp1r2 Exp2r1/ Exp2r2/ -rpkm > rpkm.txt # Use this result for gene expression clustering, PCA, etc.3. Quantify gene expression as integer counts for differential expression (-noadj)
# May also wish to use "-condenseGenes" if you don't want multiple isoforms per gene analyzeRepeats.pl rna hg19 -strand both -count exons -d Exp1r1/ Exp1r2 Exp2r1/ Exp2r2/ -noadj > raw.txt
in our case
makeTagDirectory NC_1.miRNA.tagDir/ NC_1.miRNA_hg38_mapped.sam -format sam
# raw counts
analyzeRepeats.pl /BioII/lulab_b/shared/genomes/human_hg38/gtf/miRNA.gtf hg38 -count exons -d NC_1.miRNA.tagDir/ -noadj > NC_1.miRNA.homer.counts
# calculate rpkm
analyzeRepeats.pl /BioII/lulab_b/shared/genomes/human_hg38/gtf/miRNA.gtf hg38 -count exons -d NC_1.miRNA.tagDir/ -rpkm > NC_1.miRNA.homer.rpkm
# calculate rpm/cpm
analyzeRepeats.pl /BioII/lulab_b/shared/genomes/human_hg38/gtf/miRNA.gtf hg38 -count exons -d NC_1.miRNA.tagDir/ -norm 1e7 > NC_1.miRNA.homer.rpm
Tips:
in default, homer do not use gff format file but gtf format.
look into the difference between:
- /BioII/lulab_b/shared/genomes/human_hg38/gtf/miRNA.gtf
- /BioII/lulab_b/shared/genomes/human_hg38/gtf/miRNA.gff
2.2.4 Merge to expression matrix
use linux command (cut, awk, sed, paste...)
generate expression matrix using homer:
analyzeRepeats.pl /BioII/lulab_b/shared/genomes/human_hg38/gtf/miRNA.gtf hg38 \
-d NC_1.miRNA.tagDir/ NC_2.miRNA.tagDir/ NC_1.miRNA.tagDir/ \
BeforeSurgery_1.miRNA.tagDir/ BeforeSurgery_2.miRNA.tagDir/ BeforeSurgery_2.miRNA.tagDir/ \
AfterSurgery_1.miRNA.tagDir/ AfterSurgery_2.miRNA.tagDir/ AfterSurgery_3.miRNA.tagDir/ \
-noadj > hcc_example.homer.ct.tsv
2.3 QC: Cleaning the expression matrix
* load expression matrix
# R script
> mx <- read.table("hcc_example.homer.ct.mx",sep="\t",header=T)
> head(mx[,1:5])
TranscriptID NC_1 NC_2 NC_3 BeforeSurgery_1
1 hsa-mir-631 0 0 0 0
2 hsa-mir-4635 0 0 0 0
3 hsa-mir-6761 0 0 0 0
4 hsa-mir-10a 2533 1674 2744 3564
5 hsa-mir-2276 3 2 0 1
6 hsa-mir-4468 0 0 0 0
* check the library size
> colSums(mx[,2:ncol(mx)])
NC_1 NC_2 NC_3 BeforeSurgery_1 BeforeSurgery_2
2793900 2029386 3072213 6195915 4358534
BeforeSurgery_3 AfterSurgery_1 AfterSurgery_2 AfterSurgery_3
3784022 3634594 6421256 2185529
* check total detected genes
> apply(mx[,2:ncol(mx)], 2, function(c)sum(c!=0))
NC_1 NC_2 NC_3 BeforeSurgery_1 BeforeSurgery_2
657 647 657 640 711
BeforeSurgery_3 AfterSurgery_1 AfterSurgery_2 AfterSurgery_3
679 618 651 690
* filter genes
Purpose
Filtering low-expression genes improved DEG detection sensitivity.
Methods
- Filter the genes with a total counts < = threshold;
- Filter genes with maximum normalized counts across all samples < = threshold;
- Filter genes with mean normalized counts across all samples < = threshold.
Criteria
Retain genes: (Reads >= 1 counts) >= 20% samples.
> filter_genes <- apply(
+ mx[,2:ncol(mx)],
+ 1,
+ function(x) length(x[x > 2]) >= 2
+ )
> mx_filterGenes <- mx[filter_genes,]
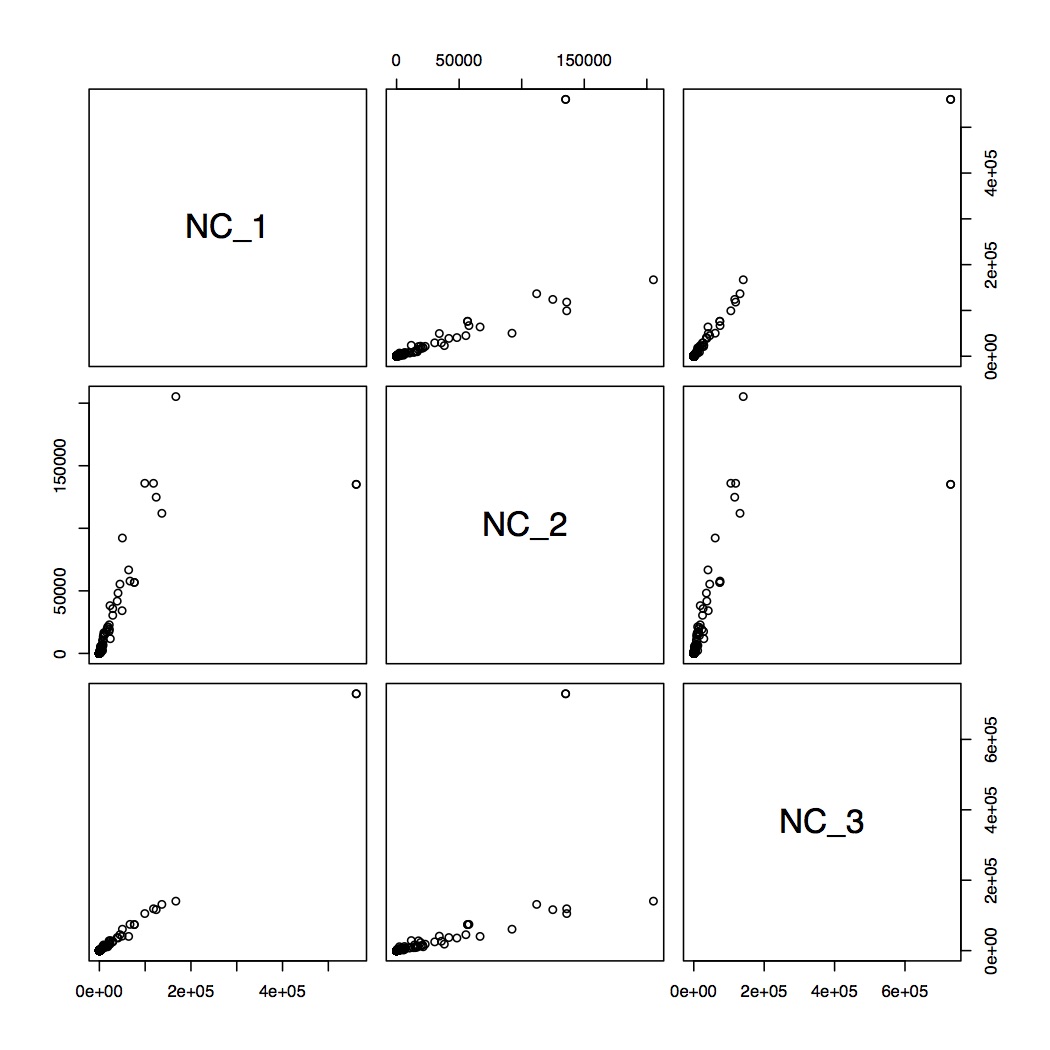
* check correlations between samples
> cor.test(mx_filterGenes$NC_1,mx_filterGenes$NC_2,methods="spearman")
> pairs(~NC_1+NC_2+NC_3,data=mx_filterGenes)
> dev.off()
Scripts summary
- convert alignments
samtools view -bhF 4 NC1.miRNA.sam | bedtools bamtofastq -i - -fq NC1.miRNA_fastq bowtie2 -p 4 --sensitive-local -x /BioII/lulab_b/shared/genomes/human_hg38/index/bowtie2_hg38_index/GRCh38_p10 NC1.miRNA_fastq -S NC1.miRNA_hg38_mapped.sam samtools view -S -b NC1.miRNA_hg38_sam > NC1.miRNA_hg38_mapped.bam - count for expression value
# use htseq htseq-count -m intersection-strict --idattr=Name --type=miRNA_primary_transcript NC_1.miRNA_hg38_mapped.sam /BioII/lulab_b/shared/genomes/human_hg38/gtf/miRNA.gff > NC_1.miRNA.htseq.counts # use featureCounts featureCounts -t miRNA_primary_transcript -g Name -a /BioII/lulab_b/shared/genomes/human_hg38/gtf/miRNA.gff -o NC_1.miRNA.featureCounts.counts NC_1.miRNA_hg38_mapped.bam # use homer analyzeRepeats.pl /BioII/lulab_b/shared/genomes/human_hg38/gtf/miRNA.gtf hg38 -count exons -d NC_1.miRNA.tagDir/ -noadj > NC_1.miRNA.homer.counts - generate expression matrix
# use homer analyzeRepeats.pl /BioII/lulab_b/shared/genomes/human_hg38/gtf/miRNA.gtf hg38 \ -d NC_1.miRNA.tagDir/ NC_2.miRNA.tagDir/ NC_1.miRNA.tagDir/ \ BeforeSurgery_1.miRNA.tagDir/ BeforeSurgery_2.miRNA.tagDir/ BeforeSurgery_2.miRNA.tagDir/ \ AfterSurgery_1.miRNA.tagDir/ AfterSurgery_2.miRNA.tagDir/ AfterSurgery_3.miRNA.tagDir/ \ -noadj > hcc_example.homer.ct.tsv - cleaning the expression matrix
# R script
> mx <- read.table("hcc_example.homer.ct.mx",sep="\t",header=T)
> head(mx[,1:5])
TranscriptID NC_1 NC_2 NC_3 BeforeSurgery_1
1 hsa-mir-631 0 0 0 0
2 hsa-mir-4635 0 0 0 0
3 hsa-mir-6761 0 0 0 0
4 hsa-mir-10a 2533 1674 2744 3564
5 hsa-mir-2276 3 2 0 1
6 hsa-mir-4468 0 0 0 0
# check library size (total mapped reads)
> colSums(mx[,2:ncol(mx)])
NC_1 NC_2 NC_3 BeforeSurgery_1 BeforeSurgery_2
2793900 2029386 3072213 6195915 4358534
BeforeSurgery_3 AfterSurgery_1 AfterSurgery_2 AfterSurgery_3
3784022 3634594 6421256 2185529
# check the number of detected genes
> apply(mx[,2:ncol(mx)], 2, function(c)sum(c!=0))
NC_1 NC_2 NC_3 BeforeSurgery_1 BeforeSurgery_2
657 647 657 640 711
BeforeSurgery_3 AfterSurgery_1 AfterSurgery_2 AfterSurgery_3
679 618 651 690
# filter genes
> filter_genes <- apply(
+ mx[,2:ncol(mx)],
+ 1,
+ function(x) length(x[x > 2]) >= 2
+ )
> mx_filterGenes <- mx[filter_genes,]
> head(mx_filterGenes[,1:5])
TranscriptID NC_1 NC_2 NC_3 BeforeSurgery_1
3 hsa-mir-6761 0 0 0 0
4 hsa-mir-10a 2533 1674 2744 3564
5 hsa-mir-2276 3 2 0 1
8 hsa-mir-100 540 165 516 2337
10 hsa-mir-371a 2 2 0 5
16 hsa-mir-3922 6 7 1 1
# check the correlations between each samples
> cor.test(mx_filterGenes$NC_1,mx_filterGenes$NC_2,methods="spearman")
Pearson's product-moment correlation
data: mx_filterGenes$NC_1 and mx_filterGenes$NC_2
t = 28.728, df = 616, p-value < 2.2e-16
alternative hypothesis: true correlation is not equal to 0
95 percent confidence interval:
0.7208567 0.7885148
sample estimates:
cor
0.7567047
> pairs(~NC_1+NC_2+NC_3,data=mx_filterGenes)
> dev.off()
# save the results
write.table(mx_filterGenes,"hcc_example.homer.ct.filtered.mx",sep="\t",quote=F,col.names=T,row.names=F)
Homeworks
scripts and files: /home/younglee/projects/bioinfoTraining/constructExpMx
Level I:
- learn how to construct the expression matrix for gencode annotations and all RNA types (miRNA, piRNA, mRNA, lncRNA...)
- compare the difference between HTSeq, featureCounts and homer
- check the bam/bigWig file using IGV
- QC and cleaning the expression matrix
Level II: - convert bam/sam files coordinates to genome coordinates
